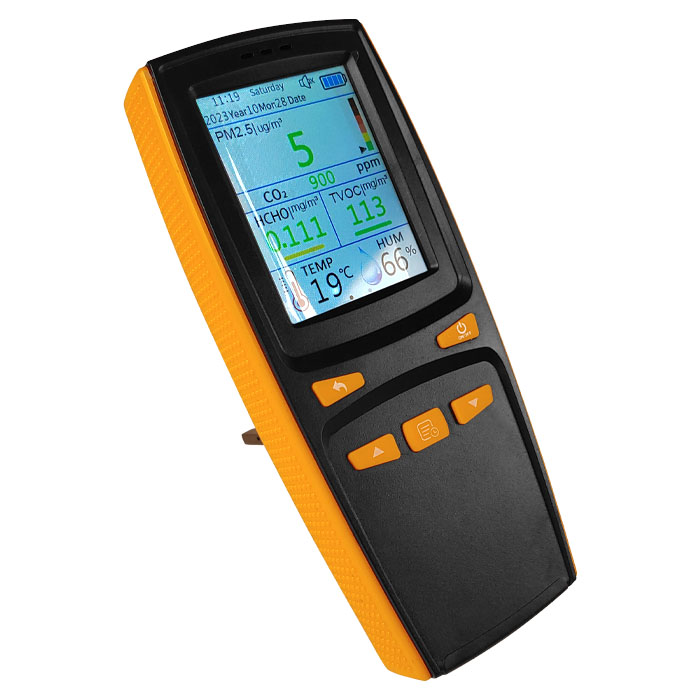
The effectiveness of air purifiers in combating fine dust and antibiotic-resistant bacteria is increasingly being researched and debated. There is concern that particulate matter in the air could play a potential role in the spread of antibiotic resistance. Studies have shown that airborne particles, including bacteria and resistance genes, may be linked to particulate matter.
This leads to the conclusion that bacteria resistant to antibiotics and the associated resistance genes could spread through the air, especially in areas with higher levels of particulate matter pollution. This alarming finding is supported by observations that have identified antibiotic-resistant bacteria and resistance genes in the air. Especially the particle size PM2.5 could play a role in airborne transmission of these bacteria and genes.
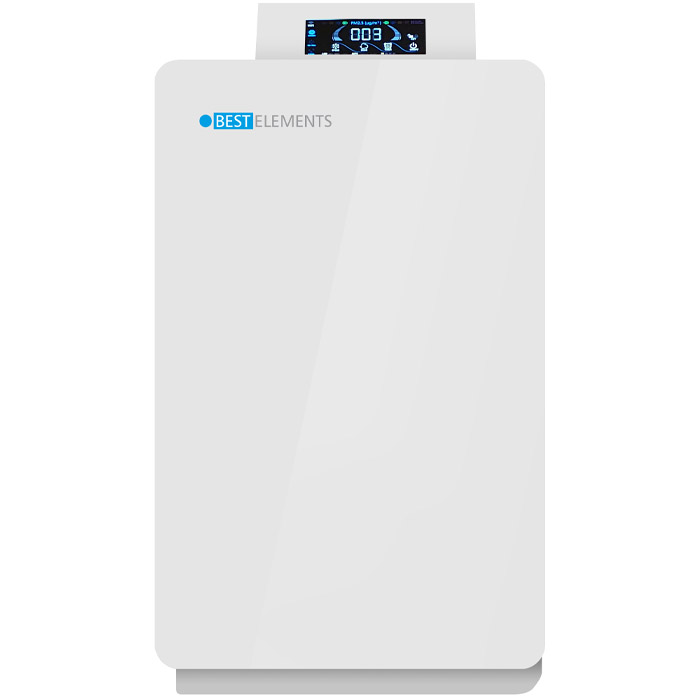
In this regard, new generations of air purifiers have received special attention. These advanced systems are able to significantly improve indoor air quality. They use multi-stage filter technologies to filter fine dust, bacteria, viruses, pollen, odors and other contaminants from the air. These latest innovations aim to increase the effectiveness of air purification and reduce the spread of bacteria and pathogens.
Air quality is not only of great importance indoors, but also in the vehicle area. Air conditioning systems in vehicles can harbor a variety of contaminants such as viruses, fungi and bacteria that pose a health hazard. Improper cleaning of air conditioners can result in poor air quality. Therefore, suitable solutions to improve air quality in vehicles are important to minimize the spread of pathogens.
Overall, the effectiveness of air purifiers in combating fine dust, bacteria and other contaminants both indoors and in vehicles is becoming increasingly important. Advances in technology and research are helping to create better solutions for improving air quality and curbing the spread of pathogens.