Molecular hydrogen has a positive effect on physical and respiratory function in acute post-COVID-19 patients: A new perspective in rehabilitation
Studies introduction
The infectious disease coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), which has emerged as a pathogen of global importance. COVID-19 is a highly contagious disease that can be transmitted through airborne droplets and contact with surfaces. Both the symptoms and the severity of the disease can vary widely in individuals, from asymptomatic but infectious to those requiring intensive care. Due to the novel emergence of SARS-CoV-2, current treatment strategies are not yet well developed and are based on the repurposing of drugs such as antiviral, immunosuppressive oxygen (O2) therapies. However, the insufficient effectiveness of these interventions is worrying.
Based on available clinical data, molecular hydrogen (H2) and hydrogen/oxygen (H2/O2 in a 2:1 ratio = Brown’s Gas) therapies have successfully treated the deleterious effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection in adults. By acting as a potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant, H2 administration may enhance recovery by inhibiting the hyperinflammatory cytokine cascade and reducing respiratory resistance in patients with symptoms of disease.
Study I
Molecular hydrogen (H2) is a therapeutic gas for patients with acute post-coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) due to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic (apoptotic cell death) and anti-fatigue properties. The aim of this study was to determine the effect of hydrogen inhalation within 14 days on the respiratory and physical fitness status of acute post-COVID-19 patients. This randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled study was conducted with pulmonary function tests and forced vital tests.
COVID-19 patients typically show clinical symptoms such as fever, headache, dry cough, shortness of breath and severe fatigue. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome is often manifested by a variety of persistent symptoms such as severe fatigue, shortness of breath, headache and attention deficit disorder, which also appear more than four weeks after the onset of COVID-19 symptoms.
This randomized, placebo-controlled study investigated whether home H2 inhalation therapy (2 × 60 minutes/day, for 14 days) can improve respiratory and body function during early recovery from acute illness in post-COVID-19 patients. The main results of this novel study were as follows:
The hydrogen inhalation showed a significant improvement. The placebo inhalation showed no improvement. The difference in improvement between H2 group and placebo group was significant.
Impaired physical fitness and long-lasting fatigue in the post-acute COVID-19 phase can have a common denominator: oxidative stress. The coronavirus induced oxidative stress and its associated negative consequences for cellular homeostasis, including redox imbalance and deterioration in mitochondrial function and ATP production, which have long been associated with both fatigue and physical fitness decline to be brought.
Hydrogen inhalation turned out to be a suitable means of treating temporary and chronic forms of oxidative stress-associated fatigue and has already been identified as a minimal clinically significant improvement in adults with chronic respiratory diseases.
Hydrogen against fatigue in healthy people and athletes
Based on the study, it can be assumed that a two-week daily H2 inhalation of acute post-COVID-19 patients led to a clinically relevant improvement in physical function. From the point of view of improved physical fitness, the anti-fatigue effect of hydrogen demonstrated in the present study has already been documented in other studies in which different types of training were examined in healthy subjects and well-trained athletes. The anti-fatigue effect of H2 is explained by its ability to stimulate oxidative metabolism, reduce oxidative stress, adjust the cellular redox environment and improve immune function. The improvements occurred regardless of gender and age.
Higher performance with H2 with the same effort
A second important finding of the present study was the similar RPE level (degree of perceived exertion) in the experimental group as well as in the control group despite different performances. The H2 group showed a clinically relevant improvement. In this situation, one would expect that higher stress would come with higher RPE. Physiological functions such as heart rate rhythm, minute ventilation and respiratory rate, muscle and joint stiffness and central fatigue were monitored. The result is a recommendation to drink hydrogen daily or inhale it. The result led to greater tolerance and resilience in the post-COVID-19 subjects.
In addition, the study results show that H2 inhalation has a positive effect on respiratory function and the H2-induced improvement in FEV1/FVC (maximum exhaled air) was associated with an increase in cardiorespiratory capacity (oxygen uptake).
Conclusions: The results demonstrate that 14-day regular H2 inhalation can be considered an efficient rehabilitation approach to improve both physical and respiratory function even in post-COVID-19 patients.
Source doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19041992 2022 mdpi.com/1660-4601/19/4/1992
Study II
Hydrogen therapy and its future prospects for alleviating COVID-19
Clinical Applications, Efficacy and Modality
The therapeutic effects of molecular hydrogen have been confirmed by numerous clinical studies and animal experiments. The results support that hydrogen inhalation can be recommended in the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia (lung infection).
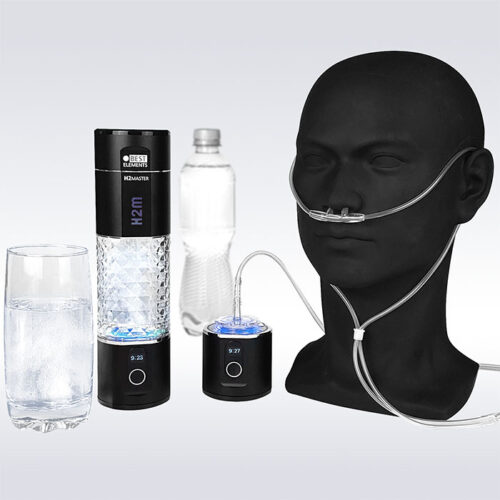
Molecular hydrogen (H2) produces a multitude of positive biological effects. A wide range of both chronic and acute inflammatory diseases, including sepsis, pancreatitis, respiratory diseases, autoimmune diseases, ischemia-reperfusion injuries, etc. can be treated and even reduced with the use of hydrogen. Hydrogen can be taken up mainly through inhalation, through hydrogen-rich drinking water which contains gaseous dissolved hydrogen, through absorption through the skin or through injection.
Hydrogen plays a crucial role as an antioxidant in immune system regulation, anti-inflammatory activities, and mitochondrial energy metabolism, and has a promising future in therapy due to its antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory benefits and universal areas of action.
In clinical studies, patients suffering from various chronic lung diseases responded very well to H2 treatments. This has confirmed that the therapeutic use of H2 is both safe and effective. In addition, it is recommended to inhale HHO, also known as Brown’s Gas, with a mixture of 66.6% hydrogen and 33.3% oxygen. H2 plays a crucial role in the prevention of lung function loss, emphysema and other lung diseases and is therefore considered an effective therapy and prevention of COVID-19 by the Health Commission on Clinical Guidelines for the Treatment of Pneumonia. The study was carried out in China.
Brown’s Gas
HHO/Browns gas more successful than pure oxygen treatment
Research in multi-center clinical trials is using a combination of hydrogen and oxygen gas (66% H2; 33% O2) produced by electrolysis of water and administered to patients with COVID-19. A significant proportion of patients in the therapy group that inhaled a mixture of H2 and O2 had improved clinical symptoms than patients in the control group that received traditional oxygen therapy.
Similarly, H2 use reduces O2, the negative effects of O2-only intake during exercise in healthy adults. Breathing a mixture of O2 and H2 can dilate the bronchioles, promoting O2 absorption through the alveoli, which carry oxygen from the air to the blood.
Symptoms occurring before therapy
Cardiovascular disorders (such as increased palpitations and irregular heartbeat), cognitive dysfunction such as anxiety, confusion, decreased cognitive function and forgetfulness, dizziness and extreme tiredness. Retinal damage: Prolonged administration of H2-saturated eye drops prevented apoptosis.
Antioxidant effect
Anti-inflammatory effect
Regulation of hydrogen (H2) and cell death
Apoptosis
Autophagy
Therapeutic administration of H2 molecules and its application in COVID-19: Inhalation of H2 for patients with COVID-19 can be an effective means to combat both oxidative stress and hypoxia. Severe COVID-19 infections require anti-inflammatory and antioxidant therapy. In combination with the previous studies, it is recommended that H2 inhalation is a potential treatment for COVID-19 by significantly reducing inflammation, apoptosis, hypoxia and oxidative stress.
It was also found that 45 minutes of daily H2 inhalation reduced airway and lung inflammation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma by increasing MCP-1, IL-6 and IL-4 levels lowered. As a result, it was found that administration of H2 in COVID-19 patients can reduce acute lung damage. Research on the long-term effects on COVID-19 and/or SARS-CoV-2 infections continues. Hydrogen in the form of inhalation as well as dissolved in gaseous form in drinking water is considered a promising therapeutic application in clinical areas as well as in the domestic area.
Other diseases of the subjects
Multiple sclerosis therapy with H2-rich drinking water can improve EAE symptoms by reducing CD4 T cell infiltration and suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokine-producing Th17 cell growth in the spinal cord. Acute kidney injury, ischemic stroke, and rheumatoid arthritis are just a few conditions where high levels of H2 have been shown to significantly enhance recovery.
Conclusion
Sources doi: PubMed Central® ncbi.nlm.nih.gov pmc PMC10377251 10.3390/biomedicines11071892 doi.org/10.3390%2Fbiomedicines11071892
Call for studies
Clinics, research institutions, organizations and institutes in Germany, DACH and the EU are called upon to create individual and further clinical studies in relation to the effectiveness of hydrogen therapies in the form of inhalation and in the form of hydrogen-rich drinking water. Contact us here.
Powerful hydrogen generators for everyday use overview
Mobile hydrogen boosters with high performance values for better personal performance
The following powerful hydrogen boosters, hydrogen filters for hydrogen-rich drinking water and hydrogen inhalers for inhaling hydrogen are very suitable for everyday use, they are certified and reliably supply our body cells with this valuable elixir of life.