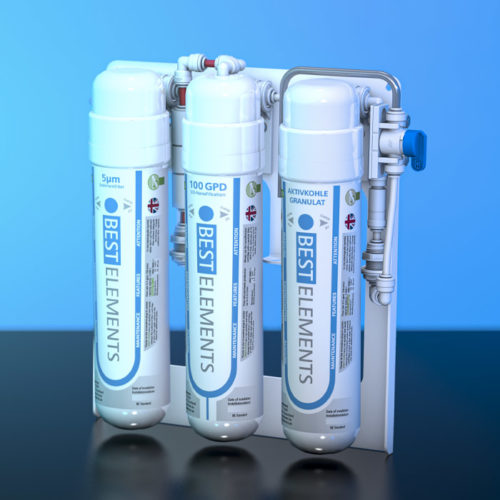
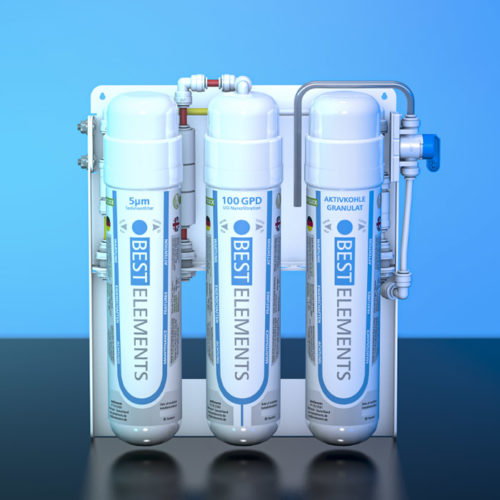
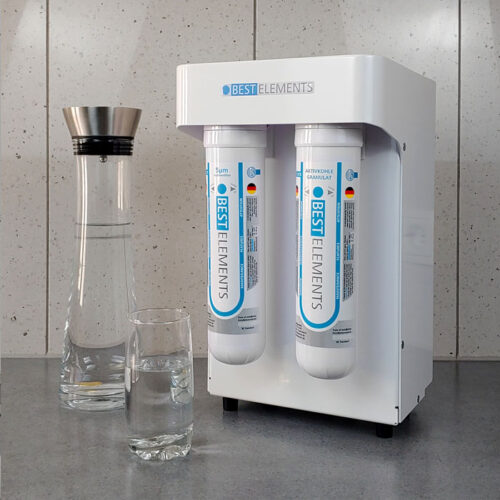
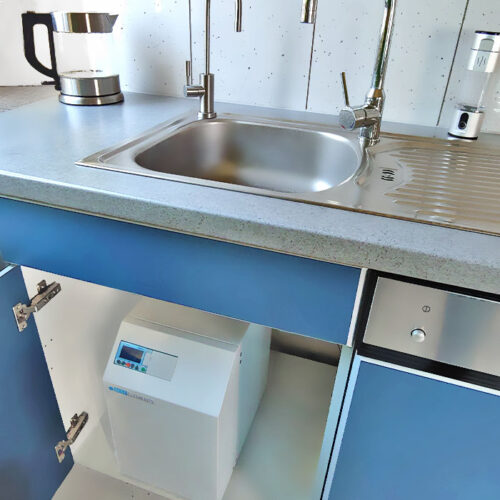
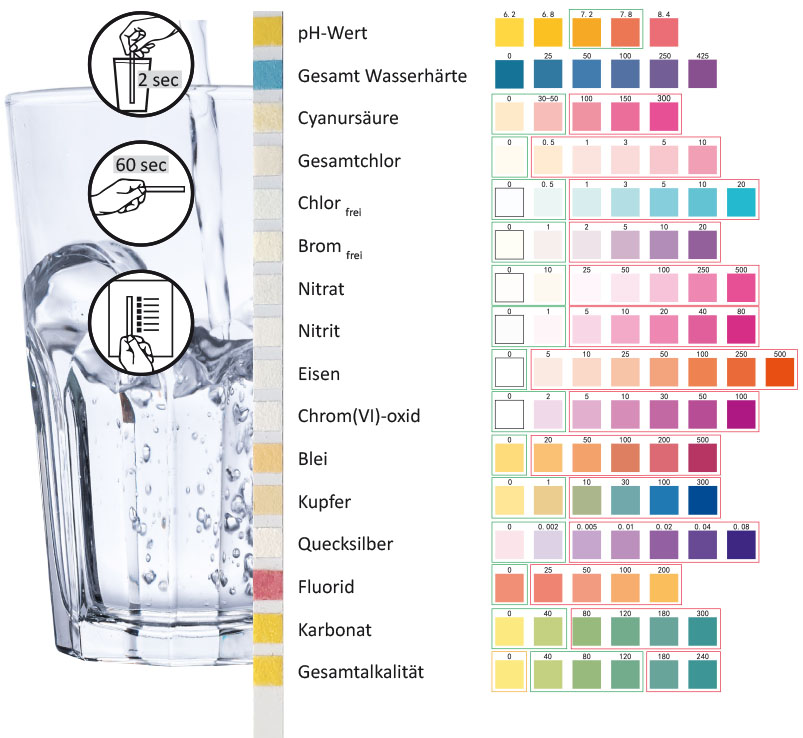
Water test readings
Application self-test water quality
- Remove a test strip and hold all measuring fields in water for approx. 2 seconds.
- Remove and leave on for 60 seconds. Remove large drops with a kitchen towel.
- Position the test strips next to the comparison fields and compare the color values.
Color fields with a green border are harmless, red border means „critical value“
Tested Values
- PH value
The pH value indicates how acidic or alkaline the water is - Total water hardness
Sum of carbonate and non-carbonate salts of calcium and magnesium - Cyanuric acid
Stabilizer for chlorine - Chlorine total
Chlorine is a disinfectant against bacteria and is considered dangerous. Too much chlorine in drinking water can irritate mucous membranes and is particularly dangerous for children, nursing mothers and pregnant women. - Chlorine free
Free chlorine refers to the level of chlorine capable of disinfecting contaminants, combined chlorine is already bound to contaminants. Total chlorine is essentially the sum of free and combined chlorine. - Bromine free
damages the nervous system and thyroid - Nitrate
Nitrogen compound that gets into the groundwater in case of over-fertilization, formation of carcinogenic nitrosamines in the body - Nitrite
Nitrites are toxic, converting to nirate, not suitable for preparing infant formula - Iron
due to corrosion and rust formation in pipe installations - Chromium(VI) oxide
highly toxic oxidizing agent - Lead
through older water pipes, particularly toxic effects on the nervous system, blood and kidneys - Copper
through water pipes, causes health disorders such as nausea, stomach pain, vomiting, intestinal colic or diarrhea - Mercury
Originating from sewage sludge on fields and natural sources, highly toxic with long-term damage to liver, kidneys, central nervous system. Visual and hearing disorders, movement disorders, irritability and psychoses are known as late effects - Fluoride
Effects on the thyroid, learning ability, memory and behavioral disorders, various sources see fluoride as a cause of reduced intelligence - Carbonate
Hydrogen carbonates of calcium and magnesium, lime/scale formation when heated or carbonic acid - Total alkalinity
Amount of alkaline substances contained in the water
pH indicates how acidic or alkaline the water is, while acidity or alkalinity is the amount of acidic or alkaline substances present in the water. For example: “Solutions with the same acidity, such as 1L0.1 mol/L hydrochloric acid and 1L0.1 mol/L acetic acid, both have an acidity of 100 mmol/L, but their pH is very different. Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid, almost 100% ionized in water, pH 1; Acetic acid is a weak acid with an ionization of only 1.3% in water and a pH of 2.9.
In the Federal Republic around 500,000 men are infertile, every fifth West German marriage remains involuntarily childless. Scientists have now discovered what could also be the reason: A whole range of dangerous chemical compounds, so-called halogenated hydrocarbons, (hydrocarbons are chemical compounds of carbon and hydrogen. If they combine with fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine, one speaks of so-called halogens) or halogenated hydrocarbons. (source “Spiegel”)
Water filters: drug residues and multi-resistant germs – water pollution
The challenge of water pollution The water in[open post...]
Lithium bisphenols and drugs in tap water: risk of autism
Drinking water from the tap contains, among other undesirable[open post...]
Water filters versus health disadvantages of mineral water and plastic bottles
"Öko-Test": Carcinogenic chromium detected in mineral water Laboratory[open post...]